This python script shows how to train a multiboost classifier on training.csv, use the score function to order the events, and determine a score threshold on a validation set. The script then classifies the events in test.csv, and creates a file called submission.csv that you can submit at the Kaggle submission site. You can execute this iPython notebook, or you can read the same notebook below (or here in a nicer format).
Running the multiboost benchmark on the Higgs boson machine learning challenge¶
import random,string,math,csv,pandas
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltTrain/validation cut and converting into arff¶
def DataToArff(xs,labels,weights,header,title,fileName):
outFile = open(fileName + ".arff","w")
outFile.write("@RELATION " + title + "\n\n")
#header
for feature in header:
outFile.write("@ATTRIBUTE " + feature +
" NUMERIC\n")
# multiboost requires ±1*weight in two columns
outFile.write("@ATTRIBUTE classSignal NUMERIC\n")
outFile.write("@ATTRIBUTE classBackground NUMERIC\n")
outFile.write("\n@DATA\n")
for x,label,weight in zip(xs,labels,weights):
for xj in x:
outFile.write(str(xj) + ",")
if label == 's':
outFile.write(str(weight) + "," + str(-weight) + "\n")
else:
outFile.write(str(-weight) + "," + str(weight) + "\n")
outFile.close()all = list(csv.reader(open("training.csv","rb"), delimiter=','))header = np.array(all[0][1:-2])xs = np.array([map(float, row[1:-2]) for row in all[1:]])
(numPoints,numFeatures) = xs.shapesSelector = np.array([row[-1] == 's' for row in all[1:]])
bSelector = np.array([row[-1] == 'b' for row in all[1:]])weights = np.array([float(row[-2]) for row in all[1:]])
labels = np.array([row[-1] for row in all[1:]])
sumWeights = np.sum(weights)
sumSWeights = np.sum(weights[sSelector])
sumBWeights = np.sum(weights[bSelector])Save/load permutation if you want to use the same cut
randomPermutation = random.sample(range(len(xs)), len(xs))
np.savetxt("randomPermutation.csv",randomPermutation,fmt='%d',delimiter=',')
#randomPermutation = np.array(map(int,np.array(list(csv.reader(open("randomPermutation.csv","rb"), delimiter=','))).flatten()))90/10 training/validation cut
numPointsTrain = int(numPoints*0.9)
numPointsValidation = numPoints - numPointsTrain
xsTrain = xs[randomPermutation[:numPointsTrain]]
xsValidation = xs[randomPermutation[numPointsTrain:]]
sSelectorTrain = sSelector[randomPermutation[:numPointsTrain]]
bSelectorTrain = bSelector[randomPermutation[:numPointsTrain]]
sSelectorValidation = sSelector[randomPermutation[numPointsTrain:]]
bSelectorValidation = bSelector[randomPermutation[numPointsTrain:]]
weightsTrain = weights[randomPermutation[:numPointsTrain]]
weightsValidation = weights[randomPermutation[numPointsTrain:]]
labelsTrain = labels[randomPermutation[:numPointsTrain]]
labelsValidation = labels[randomPermutation[numPointsTrain:]]
sumWeightsTrain = np.sum(weightsTrain)
sumSWeightsTrain = np.sum(weightsTrain[sSelectorTrain])
sumBWeightsTrain = np.sum(weightsTrain[bSelectorTrain])DataToArff(xsTrain,labelsTrain,weightsTrain,header,"HiggsML_challenge_train","training")
DataToArff(xsValidation,labelsValidation,weightsValidation,header,"HiggsML_challenge_validation","validation")Running multiboost training¶
multiboost --configfile config.txtusing config.txt. It trains AdaBoost with 3000 trees of three leaves (two inner nodes). You can change these hyperparameters in the config file:
baselearnertype SingleStumpLearner numInnerNodes
traintest training.arff validation.arff numIterations
Running till the full 3000 iterations will take hours, but you can continue executing this script after about a minute when the code starts to produce the model file shyp.xml and the table with the errors results.dta.
You can plot the learning curves (balanced weighted error rate) any time with the following command.
resultsText = list(csv.reader(open("results.dta","rb"), delimiter='\t'))
ts = [int(result[0]) for result in resultsText]
trainErrors = np.array([float(result[5]) for result in resultsText])
testErrors = np.array([float(result[11]) for result in resultsText])
fig = plt.figure()
fig.suptitle('MultiBoost learning curves', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.85)
ax.set_xlabel('number of boosting iterations')
ax.set_ylabel('balanced weighted error rate')
ax.annotate('training error', xy=(0.9*len(ts), trainErrors[len(ts)-1]),
xytext=(0.6*len(ts), trainErrors[len(ts)-1]-0.05),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='blue', shrink=0.05))
ax.annotate('validation error', xy=(0.9*len(ts), testErrors[len(ts)-1]),
xytext=(0.6*len(ts), testErrors[len(ts)-1]+0.05),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='red', shrink=0.05))
ax.plot(ts,trainErrors,'b-')
ax.plot(ts,testErrors,'r-')
ax.axis([0, len(ts), 0.1, 0.3])
plt.show()Optimizing the AMS on the held out validation set¶
s and b are the sum of signal and background weights, respectively, in the selection region.def AMS(s,b):
assert s >= 0
assert b >= 0
bReg = 10.
return math.sqrt(2 * ((s + b + bReg) *
math.log(1 + s / (b + bReg)) - s))Run
multiboost --configfile configScoresValidation.txt
using configScoresValidation.txt to output the posterior scores scoresValidation.txt on the validation set. You can change the effective number of trees used for the validation score in
posteriors validation.arff shyp.xml scoresValidation.txt numIterations
Loading the scores on the validation set
validationScoresText = list(csv.reader(open("scoresValidation.txt","rb"), delimiter=','))
validationScores = np.array([float(score[0]) for score in validationScoresText])Sorting the indices in increasing order of the scores.
tIIs = validationScores.argsort()Weights have to be normalized to the same sum as in the full set.
wFactor = 1.* numPoints / numPointsValidationInitializing 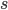 and
and 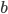 to the full sum of weights, we start by having all points in the selection region.
to the full sum of weights, we start by having all points in the selection region. amss will contain AMSs after each point moved out of the selection region in the sorted validation set. amsMax will contain the best validation AMS, and threshold will be the smallest score among the selected points. We will do len(tIIs) iterations, which means that amss[-1] is the AMS when only the point with the highest score is selected.
s = np.sum(weightsValidation[sSelectorValidation])
b = np.sum(weightsValidation[bSelectorValidation])
amss = np.empty([len(tIIs)])
amsMax = 0
threshold = 0.0
for tI in range(len(tIIs)):
# don't forget to renormalize the weights to the same sum
# as in the complete training set
amss[tI] = AMS(max(0,s * wFactor),max(0,b * wFactor))
# careful with small regions, they fluctuate a lot
if tI < 0.9 * len(tIIs) and amss[tI] > amsMax:
amsMax = amss[tI]
threshold = validationScores[tIIs[tI]]
#print tI,threshold
if sSelectorValidation[tIIs[tI]]:
s -= weightsValidation[tIIs[tI]]
else:
b -= weightsValidation[tIIs[tI]]Plotting the AMS vs the rank.
fig = plt.figure()
fig.suptitle('MultiBoost AMS curves', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
vsRank = fig.add_subplot(111)
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.85)
vsRank.set_xlabel('rank')
vsRank.set_ylabel('AMS')
vsRank.plot(amss,'b-')
vsRank.axis([0,len(amss), 0, 4])
plt.show()Plotting the AMS vs the score.
fig = plt.figure()
fig.suptitle('MultiBoost AMS curves', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
vsScore = fig.add_subplot(111)
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.85)
vsScore.set_xlabel('score')
vsScore.set_ylabel('AMS')
vsScore.plot(validationScores[tIIs],amss,'b-')
vsScore.axis([validationScores[tIIs[0]],validationScores[tIIs[-1]] , 0, 4])
plt.show()Constructing the submission file¶
Reading the test file, slicing off the header row and the id column, and converting the data into arff.
testText = list(csv.reader(open("test.csv","rb"), delimiter=','))
testIds = np.array([int(row[0]) for row in testText[1:]])
xsTest = np.array([map(float, row[1:]) for row in testText[1:]])
weightsTest = np.repeat(1.0,len(testText)-1)
labelsTest = np.repeat('s',len(testText)-1)
DataToArff(xsTest,labelsTest,weightsTest,header,"HiggsML_challenge_test","test")Run
multiboost --configfile configScoresTest.txt
using configScoresTest.txt to output the posterior scores scoresTest.txt on the test set. You can change the effective number of tree used for the test score in
posteriors test.arff shyp.xml scoresTest.txt numIterations
Reading the test scores
testScoresText = list(csv.reader(open("scoresTest.txt", "rb"),delimiter=','))
testScores = np.array([float(score[0]) for score in testScoresText])Computing the rank order.
testInversePermutation = testScores.argsort()testPermutation = list(testInversePermutation)
for tI,tII in zip(range(len(testInversePermutation)),
testInversePermutation):
testPermutation[tII] = tIComputing the submission file with columns EventId, RankOrder, and Class.
submission = np.array([[str(testIds[tI]),str(testPermutation[tI]+1),
's' if testScores[tI] >= threshold else 'b']
for tI in range(len(testIds))])submission = np.append([['EventId','RankOrder','Class']],
submission, axis=0)Saving the file that can be submitted to Kaggle.
np.savetxt("submission.csv",submission,fmt='%s',delimiter=',')